Local Memo: LLMs Send Users to 404 Pages, Users Trust Blue Links Over AI Answers, ChatGPT Relies on Scraped Google Data
Summary
A new Ahrefs study finds LLMs send users to 404 pages at higher rates than Google, research shows users still prefer blue links over AI Overviews for trust and validation, and a report uncovers ChatGPT’s reliance on scraped Google data to power timely answers.
Do LLMs Dream of 404 Pages? Ahrefs Says Yes
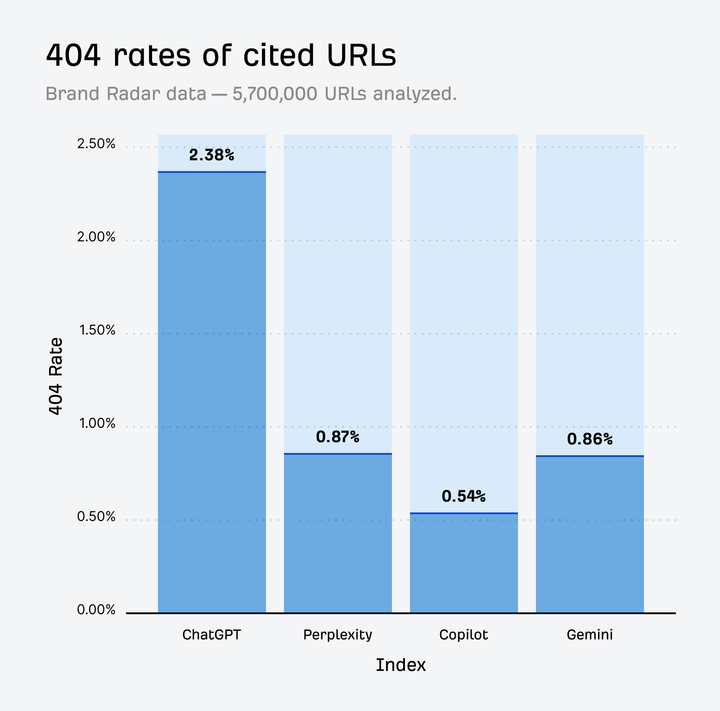
The News: A new Ahrefs study analyzing 16 million URLs found that AI assistants, particularly ChatGPT, are significantly more likely than Google Search to direct users to non-existent “404” pages.
Key findings from the study:
-
AI-generated links return 404 errors 2.87× more often than those from Google.
-
ChatGPT has the highest error rate, with 2.38% of cited URLs dead.
-
Gemini and Perplexity perform better, likely due to their reliance on Google’s search index.
-
Many of these 404s are hallucinated URLs—either expired pages remembered from training data or fabricated, plausible-looking links.
What This Means: Brands risk customers being sent to broken or fabricated links. Ensure your site has functional 404 pages that redirect users to helpful destinations instead of leaving them stranded.
Users Trust Blue Links Over AI Overviews
The News: Despite the rise of AI Overviews, trust for higher-stakes tasks still resides in traditional organic “blue links.” A new study by Kevin Indig, published on Search Engine Journal, found that while AI can handle simple queries, users still turn to authoritative sites for complex needs, transactions, or to validate AI results.
Four common user behaviors identified in the study:
-
Efficiency-First Validations: Quick fact-checks often stop at the AIO.
-
Trust-Driven Validations: Users skim the AIO but click through to trusted sources.
-
Comparative Validations: AIOs serve as a starting point, followed by exploration across multiple sites.
-
Skeptical Rejections: For high-stakes, YMYL topics, users bypass AIOs entirely in favor of trusted domains.
What This Means: SEO strategies must prioritize building trust through authoritative content. Optimizing for “high-trust moments” is essential to capture users who turn to organic results for validation.
ChatGPT Relies on Scraped Google Data
The News: While preparing for The SEO Juice webinar in April, SOCi researchers were surprised to notice that Google reviews appeared in some ChatGPT local results—despite Google’s reported refusal to grant OpenAI access to its search data.
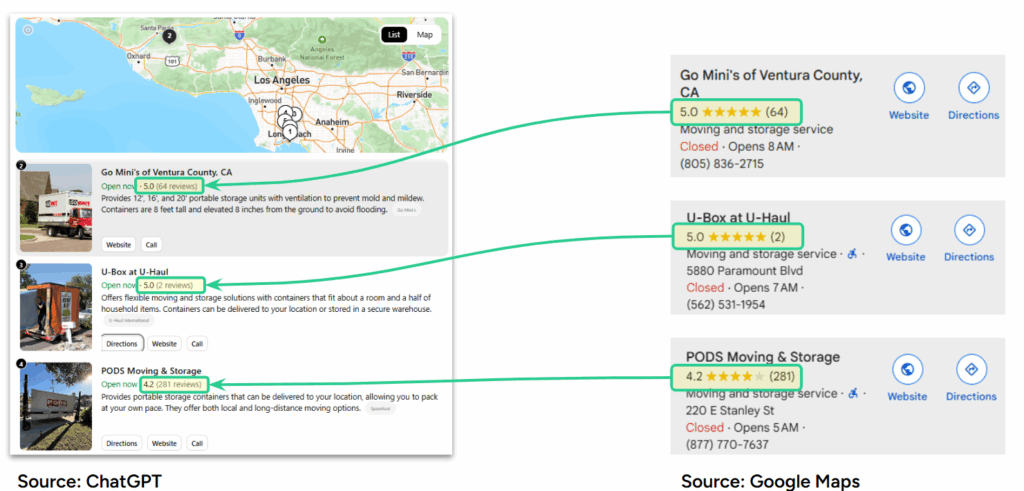
An investigation by The Information explains why. OpenAI has reportedly been using scraped Google search data via SerpApi, a third-party web-scraping firm. SerpApi listed OpenAI as a customer until May 2024, when the reference was quietly removed.
OpenAI aims to answer 80% of queries through its own search index but admits it is “nowhere near” achieving that goal. Other AI players, including Perplexity, Meta, and Apple, are also said to rely on similar third-party providers.
What This Means: Despite competitive posturing, many AI companies still depend on Google’s ecosystem. This highlights the gap between public narratives and technical realities—and reinforces Google’s central role in timely, trusted information.




