Generative Engine Optimization (GEO): Mastering AI-Driven Search in 2025
The Biggest Threat to Your Ability to Use AI? Your Broken Data Foundation
The Biggest Threat to Your Ability to Use AI? Your Broken Data Foundation
Recent SOCi data found that 82% of marketers are familiar with generative AI tools, and 65% have incorporated them into their marketing technology (MarTech) stack. Marketers have seen the potential of AI and are incorporating it into marketing strategies.
The question is, are they seeing results?
As a marketer yourself, you may be using AI. If you’re not seeing results, your broken data foundation may be holding you back. For those already seeing results, kudos! Assessing your data foundation may lead to further success.
Within this blog, we’ll discuss how marketers leverage AI, why a fragmented tech stack can hurt your AI efforts, and what you should do about it.
How Marketers Are Using AI Today
Before diving into the broken data foundation, let’s briefly revisit how marketers use AI today.

As you can see, marketers use AI in various ways, emphasizing how easily a broken data foundation can occur. A broken data foundation means information fuelling your AI is compromised. It often occurs when the underlying data supporting your strategies and decisions is flawed, incomplete, or unreliable.
Imagine constructing a skyscraper on a weak foundation — it’s a recipe for disaster. Let’s take a look at how it can hurt your efforts down the line.
How Fragmented Tech Stacks Can Hurt Your Efforts
Fragmented technology stacks can hurt AI usage through operational inefficiencies and increased costs. Data integration becomes daunting when diverse systems are developed independently to address specific challenges. The lack of communication between solutions, such as a social platform, a listings solution, and a CRM tool, results in siloed data and processes.
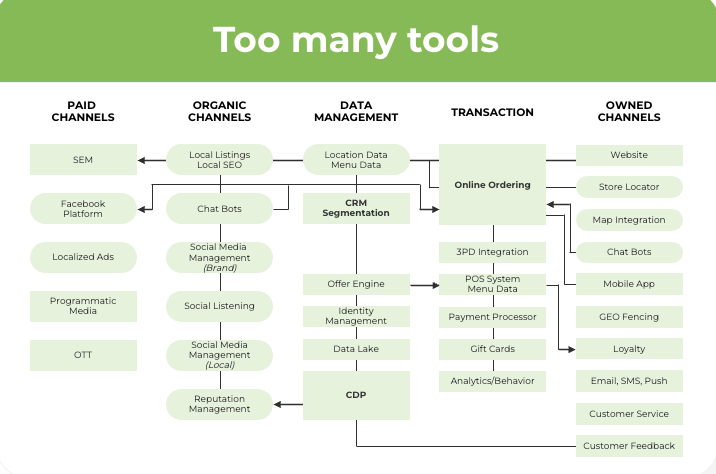
The solutions your brand uses can solve specific problems independently but often cannot integrate with other platforms, which can be competitors.
This fragmentation hinders operational agility, such as:
- Lack of fluid communication because of poor integration
- Disjointed workflows due to toggling between various applications
- Inconsistent data resulting in data inaccuracies and discrepancies
Together, these issues escalate maintenance expenses due to the complexities of managing separate systems.
How to Fix Fragmentation With One AI Layer
Introducing an AI layer over multiple solutions aims to alleviate these challenges by harmonizing data and processes. A single solution can fortify your data foundation.
However, it requires a prerequisite effort of collecting, cleaning, and normalizing your data. This data preparation is essential for AI tools to process information from various sources effectively and can be done most efficiently with a consolidated solution.
Without a concerted effort to streamline and integrate the underlying technology stack, the benefits of AI may remain unrealized, perpetuating inefficiencies and missed opportunities for your brand.
Finding the Right Solution for Your Brand
As you can see, a consolidated solution is essential when incorporating AI into your marketing efforts. When considering various solutions, there are a few things your brand should keep in mind.
For instance, which areas is your brand spending the most time on? Do the solutions you’re looking at have AI to help streamline these processes?
Does the solution allow you to scale your marketing efforts across locations while incorporating AI? These are questions you should ask yourself when navigating the buying process. For additional tips on finding the right solution for your brand, check out our CMO Planning Guide to Navigating AI Transformation in 2024.
Not sure where to start? Consider SOCi. SOCi is the CoMarketing Cloud for multi-location enterprises and provides one central place to scale and automate your marketing efforts.
Through SOCi Genius, SOCi has started adding a layer of AI automation to our marketing solutions, beginning with Genius Reviews and Genius Social. These solutions give you the solid data foundation needed to leverage AI to its fullest potential.
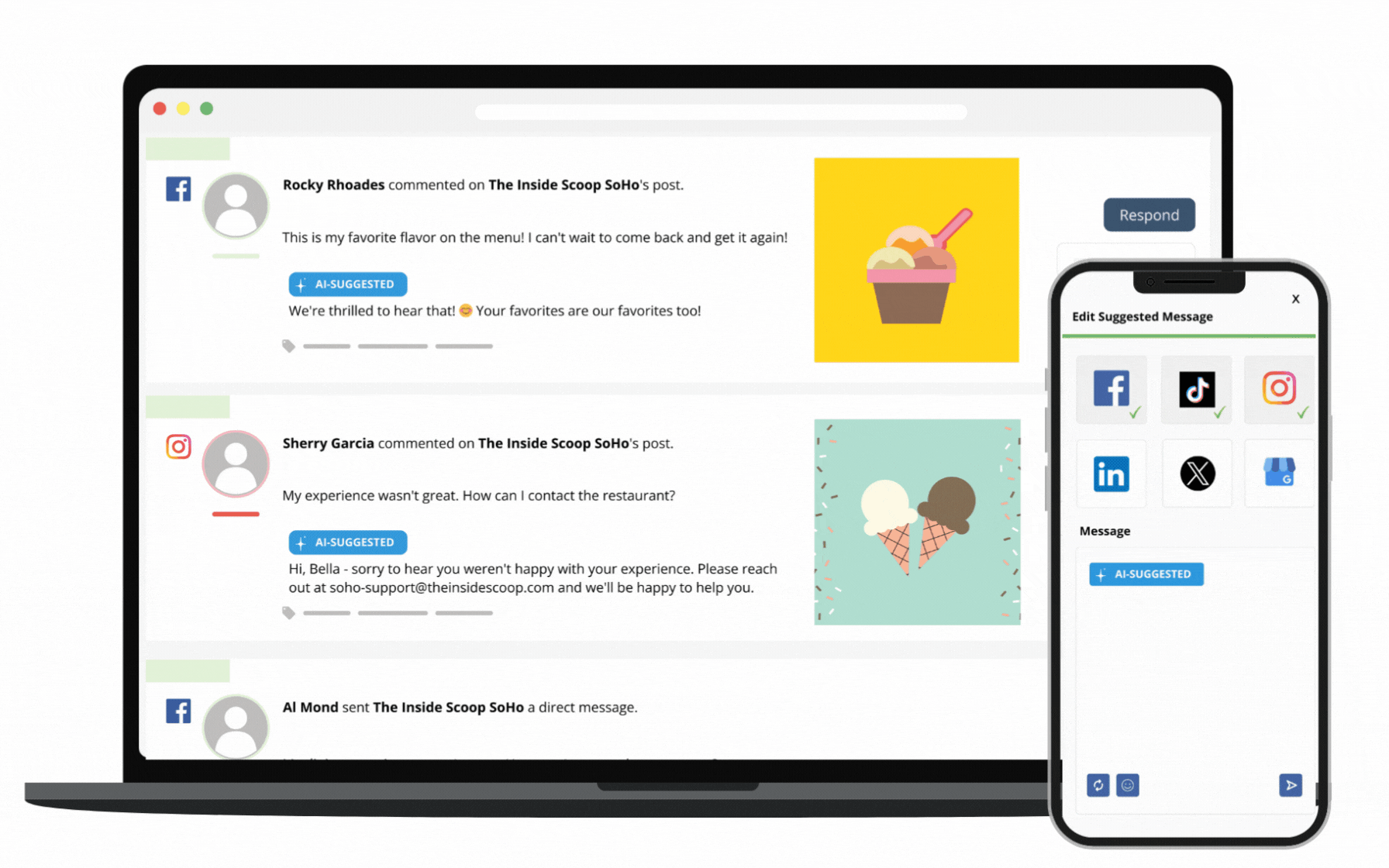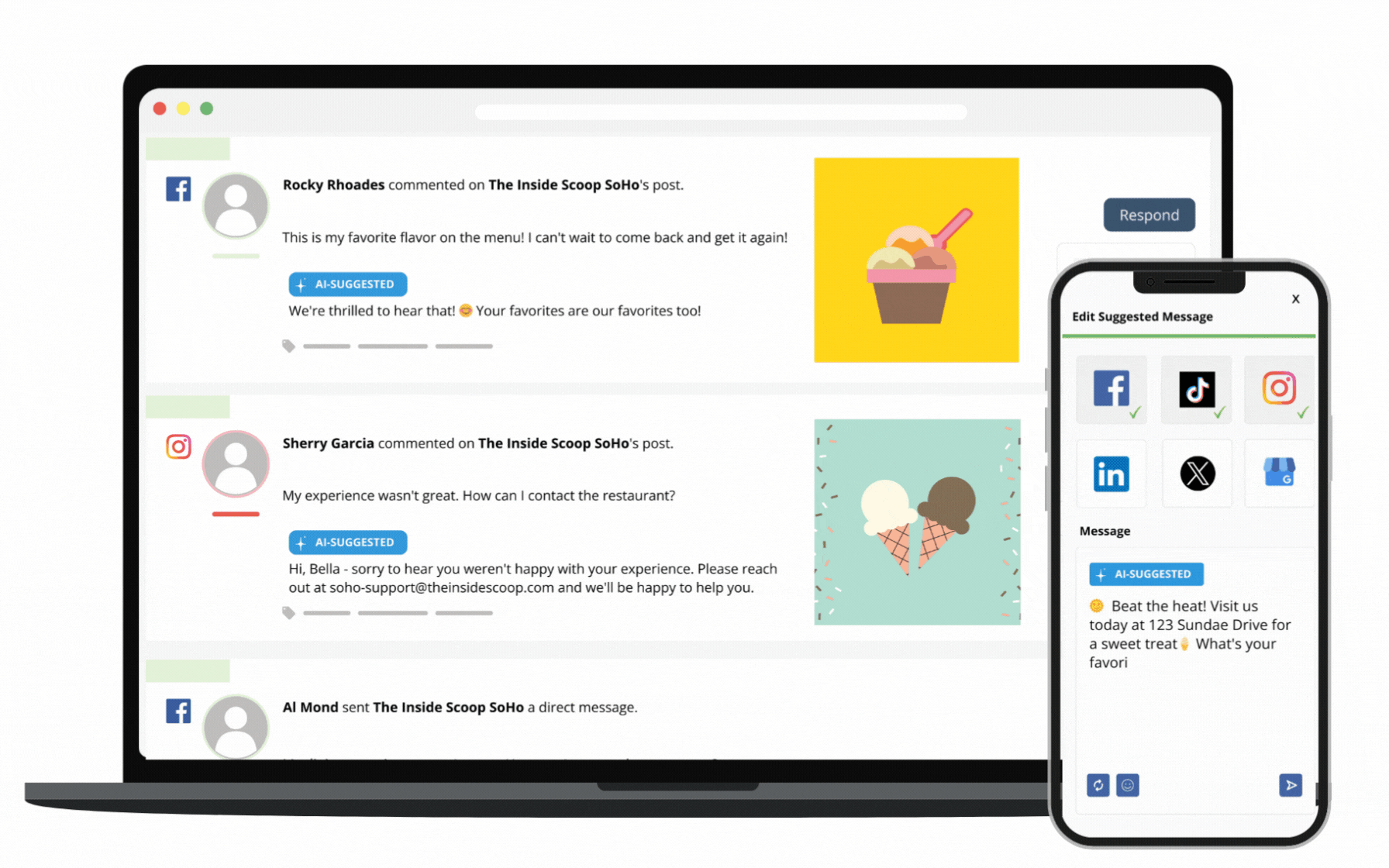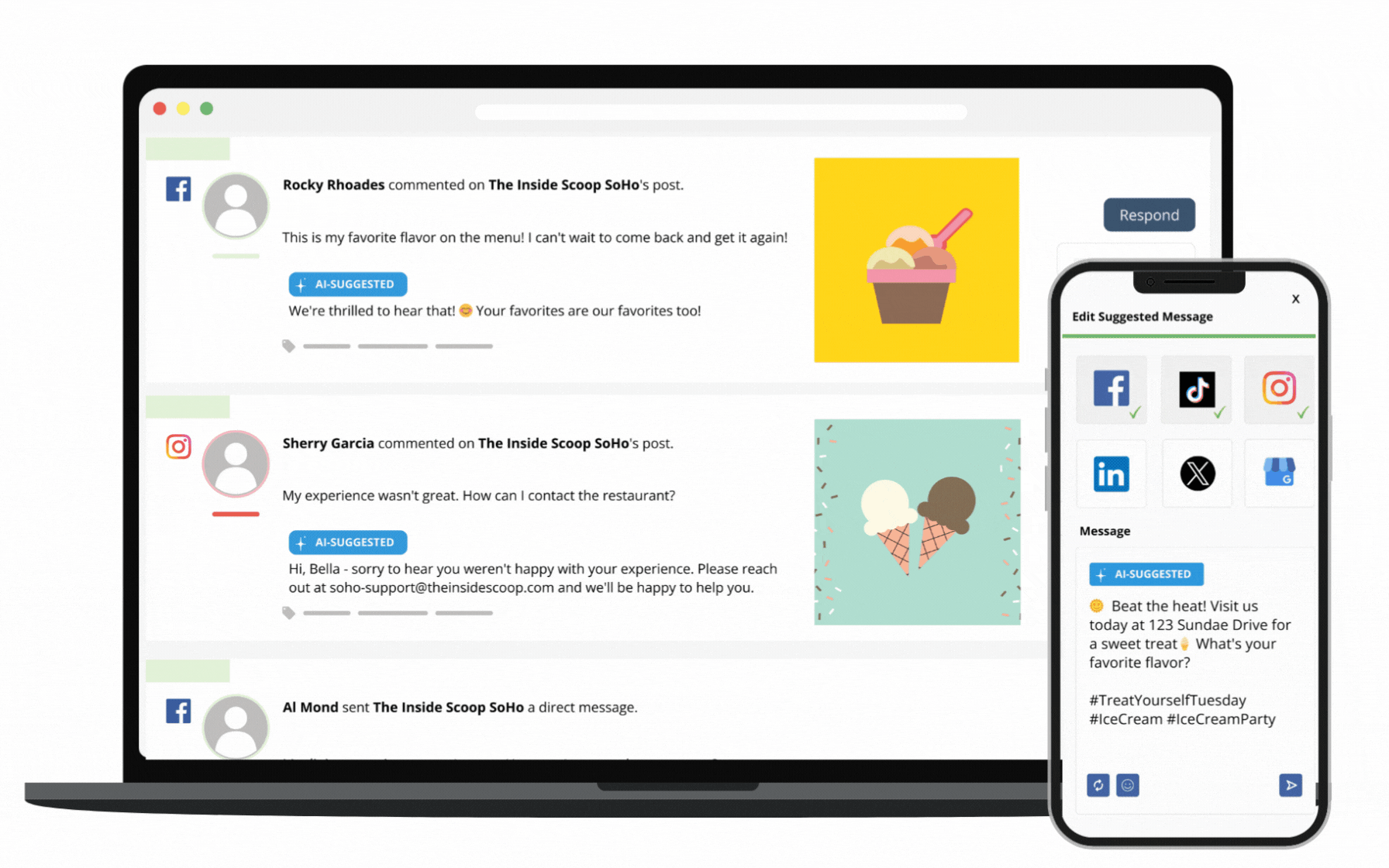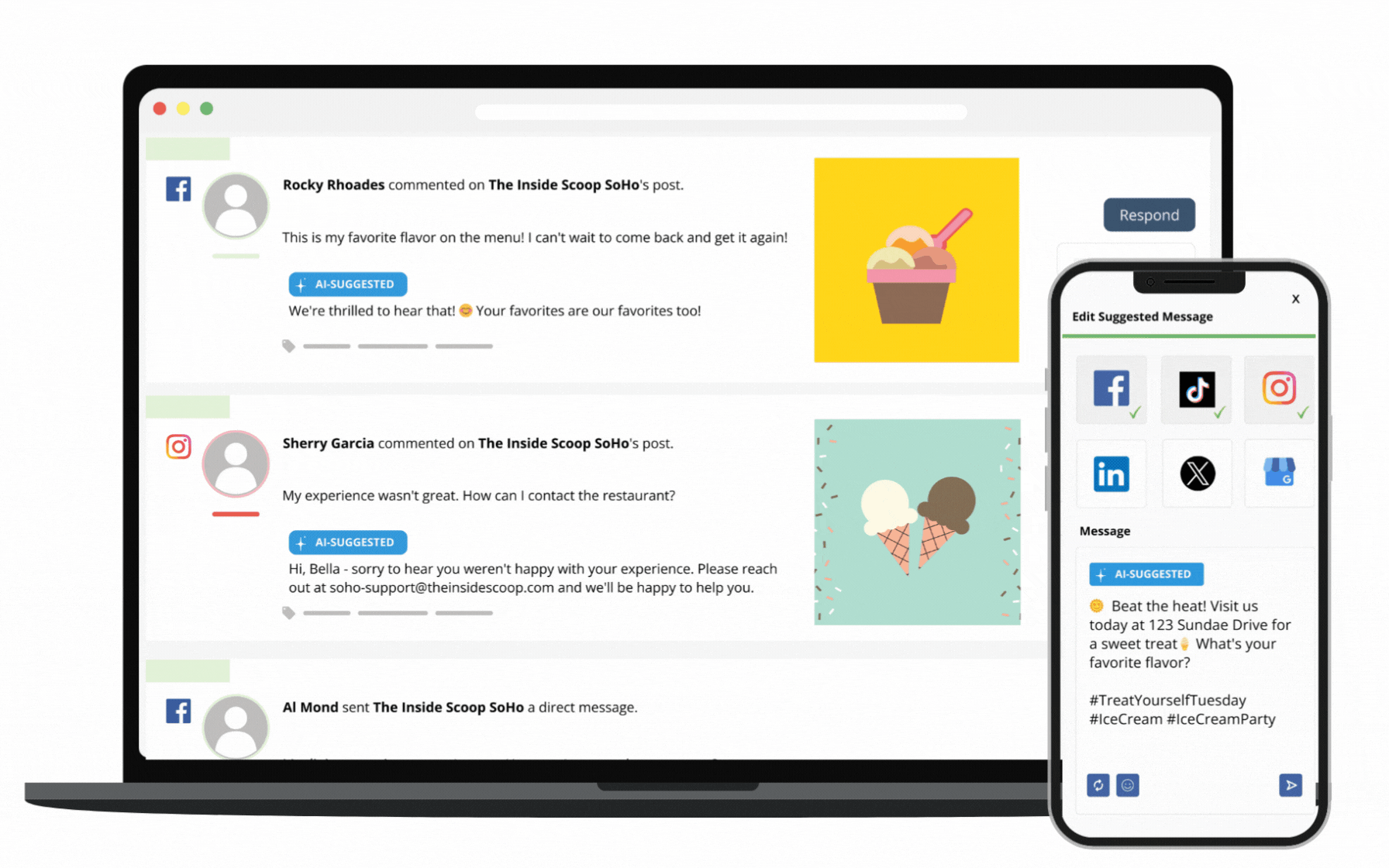
Additionally, SOCi Genius leverages advanced data science, best-in-class generative AI, “on-brand” training models, and leading localization and automation tools. Together, these abilities help you make data-driven decisions that fuel more innovative marketing strategies and increase ROI.
Ready to learn more? Request a demo today!






