Local Memo: Publisher Sues Google Over AI Summaries, GSC Reporting Shifts, ChatGPT Use Climbs
Penske Media Sues Google Over AI Summaries, What It Signals for SEO & Local Marketing
The News: Penske Media Corporation (publisher of Rolling Stone, Variety, The Hollywood Reporter, and others) has filed an antitrust lawsuit against Google. The claim is that Google’s AI-generated search summaries illegally use publishers’ reporting, siphon traffic, and reduce site visits. The lawsuit argues that this practice undermines journalism by keeping users on Google instead of sending them to original sources, all while using publishers’ content to train AI.
What This Means: For local marketing, this signals a shift from search engines as link providers to answer engines. If AI summaries dominate, fewer users will click through to business websites. Marketers will need to optimize for inclusion in AI results, focus on authority signals like reviews and backlinks, and diversify beyond Google with email, listings, social platforms, and maps to stay visible.
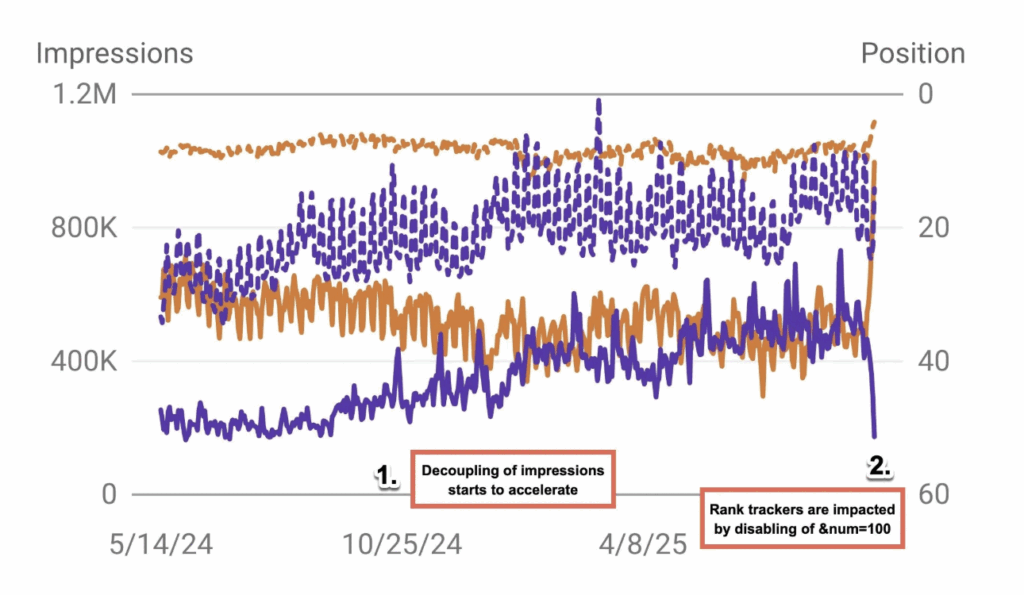
Google Search Console Reporting Off Since 100 Results Per Page Change
The News: Google removed the feature that allowed 100 search results per page. Following this change, many users are seeing big shifts in their Google Search Console (GSC) performance data. Specifically, desktop impressions have dropped noticeably, while average position metrics have increased. These changes seem tied to the 100-results-per-page removal, potentially impacting rank-tracking tools that rely on that setting.
ChatGPT Study: 1 in 4 Conversations Now Seek Information
The News: A study from OpenAI and Harvard finds that about 24% of ChatGPT conversations are now information-seeking, up from 14% a year earlier. Non-work usage has also risen to over 70%. The most common use cases are Practical Guidance, Seeking Information, and Writing.
What This Means: This study suggests people are using ChatGPT more like a search engine. Content that answers clear questions has growing importance. Brands and businesses should ensure their content is structured to provide quick, trustworthy answers that a chatbot could surface. Because a large share of usage is non-work-related, there is also value in tailoring content that appeals broadly, not only to professional or technical users. For local marketing, this shift means optimizing for conversational queries, FAQs, and “near me” style queries that match how people naturally ask for information, whether via voice, chat, or search.